Top20 Blocked Malware
| Position | Ad-Aware detection | % of all threats | Change in ranking |
| 1 | Trojan.Win32.Generic!BT | 29.18% | -2.82% |
| 2 | Win32.Trojan.Agent | 26.98% | +4.71% |
| 3 | Trojan.Win32.Generic.pak!cobra | 3.41% | +0.56% |
| 4 | Virus.VBS.Ramnit.a | 2.92% | new |
| 5 | Virus.Win32.Sality.at | 2.50% | +1.16% |
| 6 | Malware.JS.Generic | 2.21% | -1.47% |
| 7 | Trojan.Win32.Ramnit.c | 2.12% | 0.00% |
| 8 | Virus.Win32.Sality.bh | 1.97% | +0.73% |
| 9 | Virus.Win32.Ramnit.b | 1.55% | +0.1% |
| 10 | Virus.Win32.Sality.ah | 1.45% | +2.69% |
| 11 | INF.Autorun | 1.13% | +0.43% |
| 12 | HackTool.Win32.Keygen | 1.03% | -0.15% |
| 13 | Email-Worm.Win32.Brontok.ik | 0.97% | new |
| 14 | Trojan.Win32.Jpgiframe | 0.86% | +0.04% |
| 15 | Virus.Win32.Ramnit.a | 0.83% | -0.35% |
| 16 | Email-Worm.Win32.Brontok.a | 0.78% | -0.96% |
| 17 | Virus.Win32.Sality.atbh | 0.77% | new |
| 18 | Trojan-Clicker.HTML.Iframe | 0.71% | -0.14% |
| 19 | Trojan.Win32.Sirefef.bb | 0.58% | new |
| 20 | Heur.HTML.MalIFrame | 0.56% | -0.25% |
The Top 20 malicious programs blocked on PCs
March sees the increased activity of Virus.VBS.Ramnit.a, a script virus written in Visual Basic Script, previously described in a Lavasoft whitepaper published in May 2012. A modification of the ZeroAccess Trojan.Win32.Sirefef.bb has re-entered the Top 20 at position 19 suggesting a drop in prevalence compared to January. March sees a new modification of Email-Worm.Win32.Brontok.ik at position 16 and Virus.Win32.Sality.atbh at position 17. In March, INF.Autorun increased by 9 positions compared to February. Attackers continue to exploit this old method to spread malicious programs; it’s continued prevalence can be attributed to the autorun/autoplay feature on compromised machines being enabled.
New Incomings to the Lab
Let’s review and consider information on the number of unique files with the same detection name.
| Position | Ad-Aware detection | % of all threats | Change in ranking |
| 1 | Trojan.Win32.Generic!BT | 29.76% | +4.05% |
| 2 | Trojan.Win32.Generic.pak!cobra | 2.52% | +0.4% |
| 3 | Virus.Win32.Expiro.bc | 1.76% | -0.17% |
| 4 | Virus.Win32.Virut.ce | 1.38% | +0.34% |
| 5 | Trojan.Win32.Dwnldr.y | 1.30% | -0.04% |
| 6 | Trojan.Win32.Medfos.m | 1.30% | -0.05% |
| 7 | Trojan.Win32.Winwebsec.fd | 0.56% | -0.02% |
| 8 | Trojan.Win32.Vobfus.paa | 0.49% | -0.03% |
| 9 | Trojan.JS.Obfuscator.aa | 0.45% | +0.07% |
| 10 | Trojan.Win32.Tepfer.a | 0.43% | new |
| 11 | Malware.JS.Generic | 0.38% | +0.12% |
| 12 | Trojan.JS.IFrame.i | 0.37% | -0.02% |
| 13 | Worm.Win32.Mabezat.b | 0.35% | +0.04% |
| 14 | Virus.Win32.PatchLoad.d | 0.33% | +0.22% |
| 15 | Win32.Malware!Drop | 0.24% | +0.05% |
| 16 | Trojan-PWS.Win32.Zbot.aql | 0.20% | 0.00% |
| 17 | Worm.Win32.Esfury.ta | 0.18% | -0.02% |
| 18 | Trojan.Win32.Autorun.dm | 0.17% | +0.05% |
| 19 | Trojan.Win32.Generic!SB.0 | 0.14% | +0.02% |
| 20 | FraudTool.Win32.FakeRean.i | 0.15% | new |
New malicious programs entered the Top 20
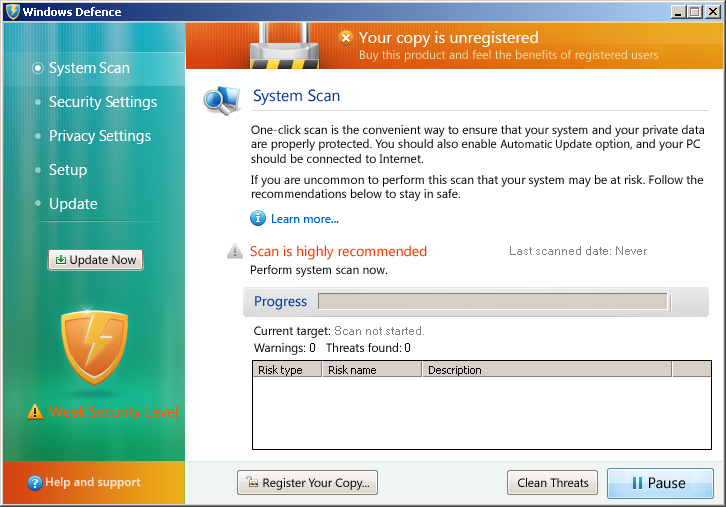
Virus.Win32.Expiro.bc entered the Top 20 at position 3 in February and remains at that position. March sees the appearance of a new Trojan program, Trojan.Win32.Tepfer.a, designed to steal user’s confidential data as well as a fake antivirus, FraudTool.Win32.FakeRean.i, entering the Top 20 at positions 10 and 12 respectively. See below for examples of FraudTool.Win32.FakeRean.i and more fake antivirus programs whose interfaces make up our Rogues gallery in March.
Fake AV (MD5: 61ea70df4955cdcd61cc8064bde3afc1) is detected by Ad-Aware as Trojan.Win32.Generic!BT
Fake AV (MD5: 33caefd51a53042c5e4c783d73a006e6) is detected by Ad-Aware as FraudTool.Win32.FakeRean.i
Fake AV (MD5: d10d8161f1b3a01bf28894eac0e553e8) is detected by Ad-Aware as FraudTool.Win32.FakeRean.i
Fake AV (MD5: 87e1e9607b2f334183f92d61b0549ccd) is detected by Ad-Aware as FraudTool.Win32.FakeSmoke
Kelihos is More Alive Than Ever
After the much publicized botnet shut down at RSA Conference , our malware analysis system registered the spam-bot using 944 public mail servers to send spam.
In March, Kelihos continues to send pharmaceutical spam e-mails:
Example of spam message sent by a bot
in an attempt to persuade users to purchase medicines to enhance sexual intimacy:
Spam emails promoting "Pengram Corporation" are also sent:
Example of spam message sent by a bot
Example of spam message sent by a bot
Trustwave SpiderLabs research shows that the botnet activity not only persists but dramatically increased after the takedown presentation. Decentralised structure of P2P botnet, packer use, and continual distribution of new modifications allow attackers to actively counteract botnet takedown attempts. Kelihos operators continue to undertake countermeasures against sinkholes.
Botnet takedowns are not a trivial task for antivirus companies, although attempts to disrupt the botnet can cause economic damage to those controlling the botnets. Efforts to disrupt botnets are hampered by ethical and privacy issues; for example, an antivirus researcher who infiltrates the botnet and issues commands to deactivate the bot software on a victim’s compromised machine is violating the victim’s privacy in the same way the botnet controller does. Furthermore, if the researcher inadvertently damages the compromised machine, the victim may attempt to take legal action against the researcher.
Targeted Attacks against Tibetan and Uyghur Activists in March
These targeted attacks have been discussed frequently, but during the last month, we noticed more references by security labs. In the middle of March, researchers from AlienVault Labs published a report describing how the attackers had been using the latest Adobe PDF exploit to attack Tibetan and Uyghur non-governmental and human rights organizations.
The malicious PDFs being sent contained exploits for the vulnerability CVE-2013-0640 which had been already patched by Adobe on the 13th of February. According to the Kaspersky Lab, the same exploit was used in the MiniDuke campaign.
Once a user opens a document, a malicious DLL is dropped into a system while a letter with the “"Noruz Bayram Merikisige Teklip” title is displayed."
According to the date stamp found inside the PDF file, it was created on 4th of February, 2013.
At the end of March, Kaspersky Lab published a report devoted to the new attack against Tibetan and Uyghur activists using Android malware.
The attack initially started with hacking the Tibetan activist’s email account. The compromised account was then used to send a spear phishing email in which attackers invite a victim to the World Uyghur Congress. The email contains the “WUC’s Conference.apk” file, a Trojan application that targets Android.
Upon installation, the application acquires the following permissions:
Once executed, the Trojan collects confidential information from a phone (phone data, contacts, location and recent victim’s calls and messages) and sends it to the C&C server (64.78.161.133):
It displays a ‘bait’ message at the same time.
The Trojan uses the “com.google.services” folder to store its files:
In addition, there are a lot of strings in the code in the Chinese language meaning that the code could be written by Chinese hackers/developers
It is thought that this is not the last attack against Tibetan and Uyghur organizations supposedly organized by the Chinese cybercriminals. Windows , MacOS and now the Android platform have been already used to run Trojans in these attacks. Which platform is going to be compromised next?
Top20 Potentially Unwanted Programs
Below are the Top20 Potentially Unwanted Programs blocked by Ad-Aware on user’s PCs. These are advertising software, browser toolbars, search engines and other programs which change browser start pages and other system settings.
| Position | Ad-Aware detection | % of all threats | Change in ranking |
| 1 | MyWebSearch | 29.31% | -0.61% |
| 2 | Win32.Toolbar.Iminent | 15.67% | +1.78% |
| 3 | Win32.PUP.Bandoo | 9.64% | +0.48% |
| 4 | SweetIM | 7.21% | -3.34% |
| 5 | Bprotector | 6.40% | -1.66% |
| 6 | Babylon | 2.74% | -1.06% |
| 7 | Yontoo | 2.23% | +0.52% |
| 8 | Wajam | 1.94% | +0.57% |
| 9 | InstallBrain | 1.90% | -0.68% |
| 10 | Artua Vladislav | 1.67% | 0.00% |
| 11 | Win32.Adware.ShopAtHome | 1.54% | -0.22% |
| 12 | Click run software | 1.47% | +0.02% |
| 13 | DownloadMR | 1.30% | new |
| 14 | GamePlayLabs | 1.29% | -0.06% |
| 15 | Vittalia Installer | 1.18% | new |
| 16 | Win32.Toolbar.Mediabar | 1.18% | -0.33% |
| 17 | Win32.PUP.Predictad | 1.14% | +0.19% |
| 18 | Win32.Toolbar.SearchQU | 1.10% | -0.1% |
| 19 | Optimum Installer | 0.81% | +0.06% |
| 20 | RelevantKnowledge | 0.76% | -0.17% |
Top20 PUPs detected on user’s PC
Operating Systems
Infections by OS
Geographic Location
Infections by country of origin
We will keep investigating the epidemiological situation in the world and informing our readers about new malicious code samples in the next Lavasoft Security Bulletin


































































































































































 69.195.129.70
69.195.129.70 Unresolvable
Unresolvable















 182.18.150.53
182.18.150.53